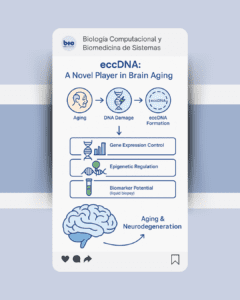
Aging is a major risk factor for neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). A growing body of research suggests that genomic instability and epigenetic alterations play a key role in these processes.
Researchers from the Computational Biology and Systems Biomedicine Research Group — Marcos J. Araúzo-Bravo and Daniela Gerovska — in collaboration with Jena University Hospital, Germany, have published a book chapter titled: “Genetic-Epigenetic Regulatory Mechanisms of Extrachromosomal Circular DNA: A New Perspective on Aging and Neurodegeneration” as part of the Springer series RNA Technologies book Decoding Aging and Neurodegeneration.
Marcos J. Araúzo-Bravo and Daniela Gerovska — in collaboration with Jena University Hospital, Germany, have published a book chapter titled: “Genetic-Epigenetic Regulatory Mechanisms of Extrachromosomal Circular DNA: A New Perspective on Aging and Neurodegeneration” as part of the Springer series RNA Technologies book Decoding Aging and Neurodegeneration.
This chapter explores the emerging importance of extrachromosomal circular DNA (eccDNA) — circular DNA fragments that exist outside chromosomes — as novel regulators of genome and epigenome dynamics in the central nervous system (CNS). Once considered mere byproducts of DNA damage, eccDNAs are now recognized for their ability to influence gene expression, chromatin architecture, and genomic stability.
The authors provide a comprehensive overview of eccDNA categorization, structural diversity, and molecular mechanisms, highlighting its roles in somatic mutations, epigenetic control, and aging-related neuronal decline. They also introduce a new computational approach, Produced per Gene Circles (PpGC), to map eccDNA sequences and reveal age-dependent genomic signatures.
These findings open the door to innovative diagnostic strategies, including the potential use of cell-free eccDNA in liquid biopsies for non-invasive monitoring of neurodegenerative disorders. By positioning eccDNA as an unconventional episomal regulator, this chapter sets the stage for new research directions in aging, CNS pathology, and biomarker discovery.
Araúzo-Bravo MJ, Gerovska D, Schwab M, Kretz A. Chapter: Genetic-Epigenetic Regulatory Mechanisms of Extrachromosomal Circular DNA: A New Perspective on Aging and Neurodegeneration in book (editor Jan Barciszewski): Decoding Aging and Neurodegeneration The Role of Nucleic Acid Epigenetics (pp.265-313) DOI:10.1007/978-3-031-91072-2_12